Pollutants
Description
This includes contaminants that result from industrial activities and consumption patterns, which are accumulating in the air, soil, waterways, and the plants and animals we eat. Companies should take a risk-based approach and work to eliminate processes and materials that result in pollutants and seek to understand the rates at which pollutants can be safely assimilated by the environment. Companies should control and limit resulting impacts on the environment and civil society.
Share this Issue on:LinkedIn
Resources
The Global Framework on Chemicals
The new Global Framework on Chemicals, adopted at the fifth session of the International Conference on Chemicals Management (ICCM5) in Bonn, Germany, provides a vision for a planet free of harm from chemicals and waste. Based around 28 targets, the framework outlines a roadmap for countries and stakeholders to collaboratively address the lifecycle of chemicals, including products and waste. It features a range of actions to ensure that a broad cross-section of stakeholders from governments, industry, international technical agencies, and civil society can support positive change on key topics, such as phasing out the most harmful chemicals, advancing circularity, and strengthening capacity-building, particularly in countries with insufficient enforcement regimes.
Practical Guide to Chemical Management Due Diligence in Supply Chains
This practical guide from the Responsible Business Alliance was created to provide you with a standardised, due diligence process template for managing chemical risks. It reflects RBA member companies’ experiences and learnings and seeks to promote a collective understanding among businesses, governments, non-governmental organisations (NGOs), workers’ organisations, employers’ organisations, the public, and other stakeholders on best practices for responsible chemical management conduct to safeguard workers’ health and the environment.
A Practical Guide For Business: Air Pollutant Emission Assessment
Developed by the Climate and Clean Air Coalition, Stockholm Environment Institute, and IKEA Group, this guide can help you to quantify air pollutant emissions within your value chain. The guide introduces a method for the comprehensive accounting of emissions and provides a six-step approach for developing an air pollutant emission inventory for a broad range of contaminants, including particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10), Sulphur Dioxide (SO2), Nitrogen Oxides (NOx), Ammonia (NH3), and Carbon Monoxide (CO). The guide also introduces approaches to mitigation and implementation, and explains how an emissions inventory can be used for decision-making and strategy.
State of Global Air Report 2025
This report from the Health Effects Institute and the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation’s (IHME’s) Global Burden of Disease (GBD) project provides reliable and meaningful information about air pollution exposure and its health effects. It features comprehensive analysis of data for air quality and health impacts for countries around the world in 2023, including trends in air pollution exposure, the continuing burden of household air pollution, and air pollution's burden of disease.
Safe planetary boundary for pollutants, including plastics, exceeded, say researchers
This article explains how - for the first time - the impact of "novel entities" (synthetic chemicals including plastics) on the stability of the Earth system has been assessed. This article will help you to understand that humanity has exceeded a planetary boundary related to environmental pollutants, and that urgent action is required.
National Geographic Resource Library: Pollution
This introductory resource provides a high-level explanation of air, land, and water pollution; key sources of pollution; and requirements for reducing pollution.
World's Air Pollution: Real-time Air Quality Index
The World Air Quality Index Project has created this interactive map to provide real-time and recent historical information on the world's air pollution in over 10,000 locations. This resource will help you to keep track of the pollution in the communities in which you operate, as well as to provide evocative air quality information to leaders for educational purposes.
A Profitable Detox: Why safer chemistry makes financial sense
This report from ChemSec can help you to understand the changes needed for a sustainable chemistry transition. It explains the the systemic risk of hazardous chemicals and outlines the mid- to long-term business case for chemical manufacturers to increase transparency, publish time-bound plans to phase out persistent chemicals, and develop safer alternatives to hazardous chemicals. It also presents tangible examples of companies that have accepted the competitive need to make this transition.
ChemForward
ChemFORWARD is a science-based, non-profit, value chain collaboration that has created a range of resources to advance safer chemistry. The Chemical Hazard Data Trust is a centralised and comprehensive repository that was designed to simplify access to chemical hazard data from credible sources; curate, maintain, and continuously improve the data; and harmonise the information for actionable decision support. ChemFORWARD's SAFER verified program assesses suppliers' trade name ingredients against rigorous human and environmental impacts using toxicology experts. The Plastic Additives Alternatives Finder supports the rapid elimination of chemicals of concern and the optimisation of plastic feedstocks with safer alternatives to accelerate circularity by enabling users to check the chemical hazard profile of over 1100 different additives used in plastics. ChemFORWARD analyses data from dozens of brands, retailers, and suppliers to produce custom Ingredient Intelligence Reports (IIRs) that provide clear, comparable data for chemical management reporting. They have also created pfasID, a free web-based tool that simplifies the process of identifying PFAS.
Towards Planet Positive Chemicals: A Chemical Transformation Roadmap
This report from the World Business Council for Sustainable Development outlines actionable steps for transforming how chemicals are produced, used, and recycled. Designed for decision-makers and stakeholders across value chains relying on chemicals (including business and sustainability leaders, policymakers, and financial institutions), the report was developed in collaboration with nine leading chemical companies and the ERM Sustainability Institute to provide a blueprint for collaboration. It identifies and unpacks three imperatives for transformation (net-zero chemicals, nature-positive chemicals, and a just transition for chemicals) and three enablers that support these imperatives (empowering a circular economy, activating sustainable chemistry, and combatting pollution). It also highlights six pathways and 33 actions to be taken by 2030 to transition toward just, net-zero, nature-positive chemicals.
WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines
This comprehensive guide was created by the World Health Organisation (WHO) for policy-makers, lawmakers, and technical experts, including industrial stakeholders and environmental impact assessment practitioners. It was created to offer quantitative, health-based recommendations for air quality, with the ultimate goal of providing guidance that can help to reduce the burden of pollutants on health worldwide. It provides specific recommendations on a range of air pollutants, including particulate matter, ozone, nitrogen and sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, and more. It also provides recommendations for implementation, monitoring, and evaluation of the guidelines.
A Beginner’s Guide to NOx, NO and NO2 as Air Pollutants
This blog provides an accessible introduction to nitrogen oxides, the differences between them, their sources, and their impact on humans and the environment.
The world's forgotten greenhouse gas
Agricultural activities may be responsible for more than a quarter of human-caused climate-warming emissions, but most of these emissions are not from carbon dioxide. The primary culprit, rather, is nitrous oxide - a compound approximately 300 times as potent as carbon dioxide at heating the atmosphere. This article explains how humanity has tipped the Earth's nitrogen cycle out of balance, and highlights solutions for runaway nitrous oxide emissions that your company can support.
What is nutrient pollution?
This brief article will introduce you to the issue of nutrient pollution from nitrogen and phosphorous, including sources of nutrient pollution and their effects on marine environments.
Planetary boundaries: balancing nutrient flows
This article provides a high-level overview of the issue of excess nitrogen and phosphorous, including key drivers; the risks to biodiversity, human health, and the climate; and the actions required to bring nutrient cycles back into balance.
Pollutants in Air and Water: A Getting Started Guide
Unmanaged and improperly managed pollutants are having a dire impact on human health and are major contributors to the global climate and nature loss crises. Increasing levels of pollution also have significant economic impacts and reduce the productivity, cleanliness, liveability, and overall resilience of communities.
Businesses have a crucial role to play in protecting people and nature. Anchored in research, our Pollutants in Air and Water: A Getting Started Guide aims to support your company as it develops a strategy to eliminate pollutants from its own operations and in its value chain.
Air pollution data portal
The WHO's Air Pollution Data Portal can help you to quickly access data and databases, factsheets, interactive tools, and key publications on ambient and household air pollution.
Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM) Knowledge Platform
The Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM) is a policy framework created to promote chemical safety around the world. Their strategic approach focuses on risk reduction; knowledge and information; governance; capacity-building and technical cooperation; and illegal international traffic. SAICM is an excellent source if you want to take a deep dive into issues related to hazardous chemicals. They have an expansive library of articles, videos, reviews, databases, e-learning resources, reports, and more on topics related to chemicals, and they lead communities of practice on a range of cross-cutting themes.
Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants
The Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants is a multilateral environmental agreement to protect human health and the environment from such harmful chemicals. This site is your one-stop shop for learning more about POPs. It provides essential information on initial and newly identified POPs; reports and decisions from the Convention; and brochures, leaflets, fact sheets, guidance manuals, and other publications.
Toxic waste, explained
This primer can help familiarise you with the topic of toxic waste, including common sources, regulations, and management.
Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: Threats to Human Health
This comprehensive report from the Endocrine Society, co-produced with the International Pollutants Elimination Network (IPEN), is an excellent resource for familiarising yourself with endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs). It provides a comprehensive introduction to EDCs; explains the impacts of EDCs and the link to endocrine disease; explains the science of EDCs, as well as detailed updates on the state of the science; and explains real world exposures to EDCs and key sources of exposure for humans, with emphasis on exposure to EDCs from four sources: plastics, pesticides, consumer products (including children’s products), and per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Freshwater: Monitoring and Regulating Water Quality
This report from the OECD can help you to better understand the environmental, human health, and economic impacts of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in freshwater. Endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) are contaminants of emerging environmental and health concern that interfere with the endocrine system in humans and wildlife, producing adverse effects such as developmental, reproductive, neurological, and immune effects. The report explains the challenge and impacts of endocrine disruptors in freshwater; considers the role of science in this context, including traditional chemical and biological analysis and effect-based monitoring; highlights policy options to reduce and manage endocrine disruptors in freshwater; and documents case studies of such new monitoring methods and explores how they can benefit water quality regulation.
Methods matter: What steps are companies taking to help curb AMR by manufacturing responsibly?
The discharge of antibiotic waste that contains active pharmaceutical ingredients into the environment is a key driver of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). It explores the current state of play and highlights three actions that your company can take to manufacture responsibly, including employing effective methods to reduce AMR risks; promoting compliance with discharge limits across the supply chain; and transparently disclosing responsible manufacturing practices.
Technical Brief on Water, Sanitation, Hygiene, and Wastewater Management to Prevent Infections and Reduce the Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance
Although improvements in water sanitation and hygiene (WASH) and wastewater management in all sectors are critical elements of preventing infections and reducing the spread of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), WASH and wastewater management actors and improvement actions continue to be under-represented in AMR multi-stakeholder platforms and national action plans (NAPs). This technical brief from the WHO, the Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO), and the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) provides a summary of evidence and rationale for WASH and wastewater actions within AMR NAPs and sector-specific policy to combat AMR. Evidence and actions are presented in the domains of six key action areas: coordination and leadership; households and communities; healthcare facilities; animal and plant production; manufacturing of antimicrobials; and surveillance and research. This resource will be especially beneficial for change agents that want to build their understanding (and the case) for supporting WASH- and wastewater management-related actions in the areas where they operate.
PAS 2090:2025 Pharmaceutical products – Product category rules (PCR) for environmental lifecycle assessments – Specification
This 'Publicly Available Specification' (PAS) from the British Standards Institution (BSI) can help you to better understand and share information on the environmental impacts of medicines and to improve drug designs and manufacturing processes. It is the world's first global standard to offer a harmonised, practical, flexible framework for measuring and assessing the impact of pharmaceutical products throughout their lifecycle, including across their manufacture, supply, use, and disposal.
Why does AMR matter?
This short primer from the UN Environment Programme can help acquaint you with the concept of antimicrobial resistance and its growing impact on global society.
Forecasting the Fallout from AMR: Economic Impacts of Antimicrobial Resistance in Humans
This tool from the Centre for Global Development can help you to explore the potential impact of different interventions to combat antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Adjusting the controls in the left-hand sidebar allows you to visualise the economic and health impacts of AMR across different regions, income groups, and countries; compare the effectiveness of various interventions, such as developing new antibiotics and improving infection prevention and control; and understand the potential return on investment in combating AMR. This tool also features a comprehensive report with detailed analyses and methodology. This resource will be particularly beneficial to sustainability professionals that want to build a case for taking action on AMR.
Bracing for Superbugs: Strengthening environmental action in the One Health response to antimicrobial resistance
This report from UNEP can help you to understand how the environment plays a key role in the development, transmission, and spread of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). It unpacks the different - yet interconnected - aspects of the environmental dimensions of AMR and provides actionable evidence of the importance of the environment in the development, transmission, and spread of AMR. It explains that environmental dimensions of AMR are multifaceted and that the response rests on collaboration between sectors, and champions a concerted systems approach such as “One Health” for managing, preventing, and responding to AMR. One Health recognises that the health of people, animals, plants, and the environment are closely linked and interdependent. Against the backdrop of One Health, the report analyses three sectors and their value chains that are key drivers of AMR development and spread in the environment: pharmaceuticals and other chemicals, agriculture and food, and healthcare, together with pollutants from poor sanitation, sewage and waste effluent in municipal systems. The report synthesises current knowledge gaps, explains further work that needs to be done, and offers solutions to prevent and respond to AMR. This guide will be especially beneficial to risk, sustainability, and strategy professionals, and particularly those working in - or immediately adjacent to - the aforementioned sectors.
Antimicrobial Resistance
This fact sheet from the World Health Organisation (WHO) explains the present situation of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) globally; coordinated global action to address AMR; and the programmatic response to AMR in countries. This resource will be especially beneficial to senior leaders who want to quickly grow their understanding of the state of play of AMR.
Global Database for Tracking Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Country Self-Assessment Survey (TrACSS)
This global database can help you to track the progress of countries in addressing antimicrobial resistance. Jointly developed by the Quadripartite (FAO, UNEP, WHO and WOAH) and administered annually by the World Health Organisation, TrACSS monitors the implementation of multisectoral AMR national action plans. It features an interactive map with a range of topic layers, including human health, animal health, and food and agriculture. The database also features data comparisons and country profiles.
Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS)
The WHO launched the Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) in 2015 to strengthen knowledge on AMR, continue filling knowledge gaps, and inform strategies at all levels. GLASS is the first global collaborative effort to standardise AMR surveillance, such as providing a standardised approach to the collection, analysis, interpretation, and sharing of data by countries, territories, and areas. It also monitors the status of existing and new national surveillance systems.
AMR Industry Alliance
The AMR Industry Alliance is one of the largest private sector coalitions established to provide sustainable solutions to curb antimicrobial resistance. Comprised of over 100 biotech, diagnostics, generics, and research-based pharmaceutical companies and associations, the alliance publishes progress reports, standards and principles, case studies, and other helpful resources.
Metals: A Getting Started Guide
Despite decades of international action, exposure globally to toxic metals is pervasive and persists at crisis levels, and businesses have a crucial role to play in protecting people and nature from metal pollutants.
Anchored in research, our Metals: A Getting Started Guide aims to support your company as it develops a strategy to eliminate metal pollutants from their own operations and in their value chains.
Protocol on Heavy Metals
The 1998 Aarhus Protocol on Heavy Metals provides strict limits on cadmium, lead, and mercury emissions. It outlines best available techniques for reducing such emissions from industrial sources, combustion processes, and waste incineration, and also introduces measures to reduce and manage heavy metal emissions from products such as batteries, measuring devices, pesticides, and paint.
Heavy Metals Toxicity and the Environment
This resource is a helpful primer on arsenic, cadmium, chromium, lead, and mercury - five priority metals of public health significance. For each metal it explains environmental occurrence, industrial production and use, the potential for human exposure, and mechanisms of toxicity and carcinogenicity.
The Minamata Convention on Mercury
This international treaty, first signed in 2013 by 140 countries, is designed to protect human health and the environment from the dangers of widespread mercury pollution. The treaty requirements cover the entire life cycle of mercury, including phasing out mercury use in products and manufacturing processes (e.g. batteries and pesticides), banning new mercury mines (e.g. small-scale gold mining), limiting the emission of mercury into the environment (e.g. coal burning), and decontaminating sites. The annex also provides a breakdown of all goods and processes affected by the agreement. This document will be most useful to sustainability and supply chain management teams that want to build their understanding of mercury-related regulations and how they might relate to your organisation and value chain.
Guidance on the Management of Contaminated Sites
This guide by the UN Environmental Programme can help you remediate mercury contaminated sites in line with article 12 of the Minamata Convention. It begins with an introduction to the issue of mercury pollution and a summary of remedial obligations agreed upon by signatories of the Convention. It then provides practical guidance on identifying contaminated sites, engaging the public, and assessing risk to human health and the environmental. It also covers different options to manage and remediate contamination. The final sections outline how to evaluate the costs and benefits of taking action and how to verify efficacy. This guidance will be most useful to environmental health and safety (EHS) and engineering departments.
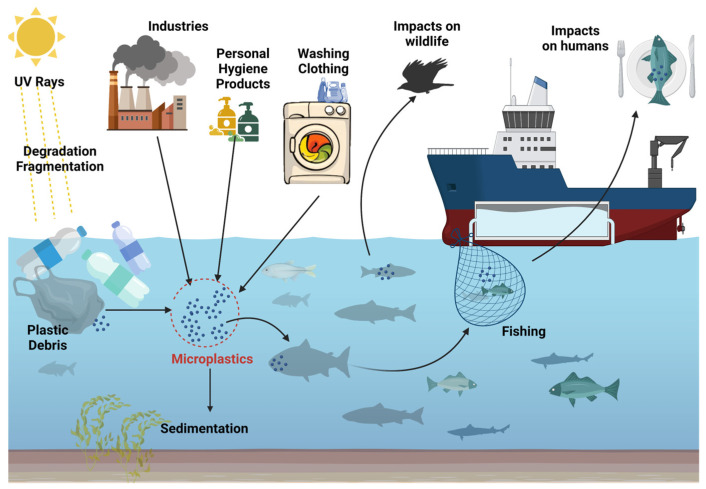
Microplastics: A Real Global Threat for Environment and Food Safety: A State of the Art Review
This comprehensive article can help you to build a deeper understanding of microplastics. It explains key sources of microplastic particles; humanity's problematic management of plastic waste; the potential effects of microplastics on human and animal health; and solutions for reducing microplastic pollution. This resource will be especially beneficial to sustainability professionals responsible for highlighting impacts and material risks, as well as for educating senior leaders.
Everything you should know about microplastics
This article from UNEP is a good primer for leaders that want to better acquaint themselves with the issue of microplastic pollution. It explains microplastics, key sources of pollution, methods for reducing their presence in the environment, and more.
Microplastics are in our bodies. How much do they harm us?
This article from National Geographic can help you to better understand the scope and scale of harm caused by microplastics in the bodies of both humans and animals.
Microplastics are in the air we breathe and in Earth’s atmosphere, and they affect the climate
Microplastics can be found in every environmental system on the planet, and are making their way into the food we eat, the water we drink, and - increasingly - the air we breathe. Looking beyond the immediate health consequences, this article (and accompanying report) can help you to understand how airborne microplastics behave in the atmosphere and how they contribute to climate change.
Microplastics are raining down from the sky
This explainer from National Geographic can help you to understand the extent of airborne microplastic and nanoplastic particulate pollution, and the implications they may have on human health and the environment.
Getting to the Heart of the (Particulate) Matter
The World Health Organisation estimates that more than 99% of the world’s population breathes air that exceeds its health-based air quality guideline limits, and that millions of premature deaths can be attributed annually to breathing in air pollution. This explainer from NASA can help you to understand the scale and scope of the air pollution crisis, and especially of the dangers of particulate matter. It explains the nature and sources of particulate matter pollution; outlines the implications for human health; and highlights the efforts that are underway to determine the types and sources of particulate matter most harmful to humans.
The Plastic Leak Project Guidelines
This comprehensive publication provides the first science-based methodology to map and measure plastic leakage across corporate value chains. Part of the Plastic Leak Project, this document will provide sustainability managers and corporate decision-makers with a framework for understanding where (and how much) leakage is occurring, and can help you to create impactful strategies and actions that effectively address plastic pollution and mitigate key business risks. Also available is a Plastic Leak Project Brief, which provides decision-makers with an overview of the guidelines, a summary of the challenges they help address, the business value of this metrics-based approach to building a plastics strategy, and more.
Asbestos Information
This is a good source of information on the basics of asbestos. It explains what asbestos is, how it's used, and the effects it can have on human health.
Air Quality Stripes
This resource can help you to better visualise and explain key trends in particulate pollution. Inspired by the Climate Stripes, these air quality stripe images show the change in particulate matter (PM2.5) air pollution from 1850 to 2021 in cities around the globe.
The WELL Air concept
The WELL Air concept was created to promote indoor air quality through a diverse range of holistic design strategies aimed at reducing harmful exposure to contaminants. This guidance addresses a broad array of topics that can help you to improve the air quality in your facilities, including ventilation design, pollution infiltration management, air quality monitoring and awareness, and microbe and mold control.
Volatile Organic Compounds' Impact on Indoor Air Quality
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are gaseous emissions from certain solids or liquids that may have short- and long-term impacts on human health. This page from the Environmental Protection Agency can help you to become familiar with the sources of VOCs, their health effects, and steps to reduce exposure.
Air Emissions and Ambient Air Quality
These environmental, health, and safety guidelines from the International Finance Corporation apply to facilities or projects that generate emissions to air at any stage of the project life-cycle. It is intended to complement industry-specific emissions guidance presented in the Industry Sector Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Guidelines by providing information about common techniques for emissions management that may be applied to a range of industry sectors; providing an approach to the management of significant sources of emissions; providing specific guidance for assessment and monitoring of impacts; and providing additional information on approaches to emissions management in projects located in areas of poor air quality.
What is Radiation?
This simple primer can help you to understand what radiation is, including the types of radiation and how they differ.
Radiation and Health
The World Health Organisation has developed evidence-based guidance, tools, and technical advice and information on public health issues related to ionising and non-ionising radiation, with a focus on electromagnetic fields, environmental radiation exposure, medical radiation exposure, optical radiation, norms and standards, and radiation emergencies.
Ionizing radiation and health effects
This fact sheet from the World Health Organisation (WHO) can help you to understand ionising radiation, including key sources of radiation, pathways to exposure, and the effects of exposure on human health.
Compendium of WHO and other UN guidance on health and environment - Radiation
This guidance from the UN features overviews for UV radiation, electromagnetic fields, radiation exposure in healthcare, radon, radioactivity in food and drinking-water, and radiological emergencies, as well as information on key policies, actions, awareness raising, and capacity building.
Radon Fact Sheet
This fact sheet from the World Health Organisation can help to familiarise you with the health effects of radon; the risk of radon in buildings and in water; and actions for reducing radon in indoor settings.
Radon database
This database from the World Health Organisation provides information on radon reference levels; concentration measurements; prevention and mitigation; action plans and regulations; and more.
Noise Pollution
Noise pollution impacts millions of people on a daily basis, as well as innumerable animals on land and in marine and freshwater environments. This short explainer can help you to understand what noise pollution is; the effects it can have on wild species; and common sources of noise pollution.
Compendium of WHO and other UN guidance on health and environment: Environmental noise
This resource features a range of information on the effects of noise on human health and nature. It provides limits for acceptable noise exposure for humans and provides a table with guidance for addressing common sources of noise pollution.
Revised Guidelines for the Reduction of Underwater Radiated Noise from Shipping to Address Adverse Impacts on Marine Life
These guidelines from the International Maritime Organisation were created to provide an overview of approaches applicable to designers, shipbuilders, and ship operators for reducing the underwater radiated noise (URN) of any given ship, as well as to assist relevant stakeholders in establishing mechanisms and programmes through which noise reduction efforts can be realised. It provides information on URN management planning, URN reduction approaches, evaluation and monitoring, and more.
Who pollutes the ocean with noise?
This short article from Ocean Care provides a summary of key ocean noise-generating activities, including shipping, seismic activities from oil and gas exploration, military activities, pile driving and construction, and deep-sea mining.
How Does Noise Pollution Harm Marine Species?
This short article explains some of the negative effects that underwater noise can have on marine mammals, including physical injuries, changes in behaviour, and communication interference.
The Impact of Ocean Noise Pollution on Fish and Invertebrates
This report from Ocean Care provides a review of 115 primary studies encompassing various human-produced underwater noise sources on dozens of species of fish (including herring, tuna, halibut, rockfish, and bass) and invertebrates (including octopi, squid, jellyfish, shrimp, lobsters, and shellfish). It explains how noise can affect an individual’s behavior, physiology, anatomy, and development, with potentially significant impacts on reproduction, health, and mortality.
Deep-Sea Mining: A noisy affair
This report from Ocean Care can help you to build your understanding of underwater noise emissions from deep-sea mining (DSM) activities. It provides an overview of human-caused underwater noise, explains the state of knowledge in regard to noise emissions from deep-sea mining activities, and explains their impact on marine life. It also provides an overview of legal and policy frameworks.
Best Available Technology (BAT) and Best Environmental Practice (BEP) for Mitigating Three Noise Sources: Shipping, Seismic Airgun Surveys, and Pile Driving
This report from the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS) and Ocean Care provides a comprehensive overview of (current) best available techniques, technologies, and practices for preventing and reducing marine noise pollution from shipping, air guns, and pile driving.
Our nights are getting brighter, and Earth is paying the price
This fascinating and heartfelt article can help you to better understand and appreciate the growing problem of light pollution, and the long-term effects it is having on humans and nature.
Illuminating the Effects of Light Pollution
This article may be useful as part of an executive primer on the effects of light pollution, highlighting evocative examples such as bird collisions, algae blooms, and beached baby turtles.
The dark side of light: how artificial lighting is harming the natural world
Artificial lighting within towns and cities, along roads and highways, and at business sites is so pervasive that it can be easy to overlook or underestimate their effect on ecosystems. This article from Nature can help you to understand the profound impact that light pollution is having on ecology, such as migrational species and insects, as well as the results of experiments conducted to identify harm reduction alternatives.
National Light Pollution Guidelines for Wildlife
This resource from Australia's Department of the Environment and Energy provides a framework that can help you to assess and manage the impact of artificial light on susceptible wildlife. It introduces a multi-step approach that explains how artificial light impacts wildlife; highlights the principles of best practice light design; explains how to determine biologically relevant luminance and perform artificial light auditing; and provides an artificial light management checklist. The guidance also features species-specific appendices and case studies.
The International Dark-Sky Association: Light Pollution
The International Dark-Sky Association is a non-profit organisation committed to preserving and protecting the night-time environment and shared heritage of dark skies. Their website provides a wide array of information to grow your understanding of the causes and effects of light pollution, with themes specific to wildlife and ecosystems, energy waste, human health, and the intersection of lighting, crime, and safety. Their resources also include videos, infographics, and a research library.
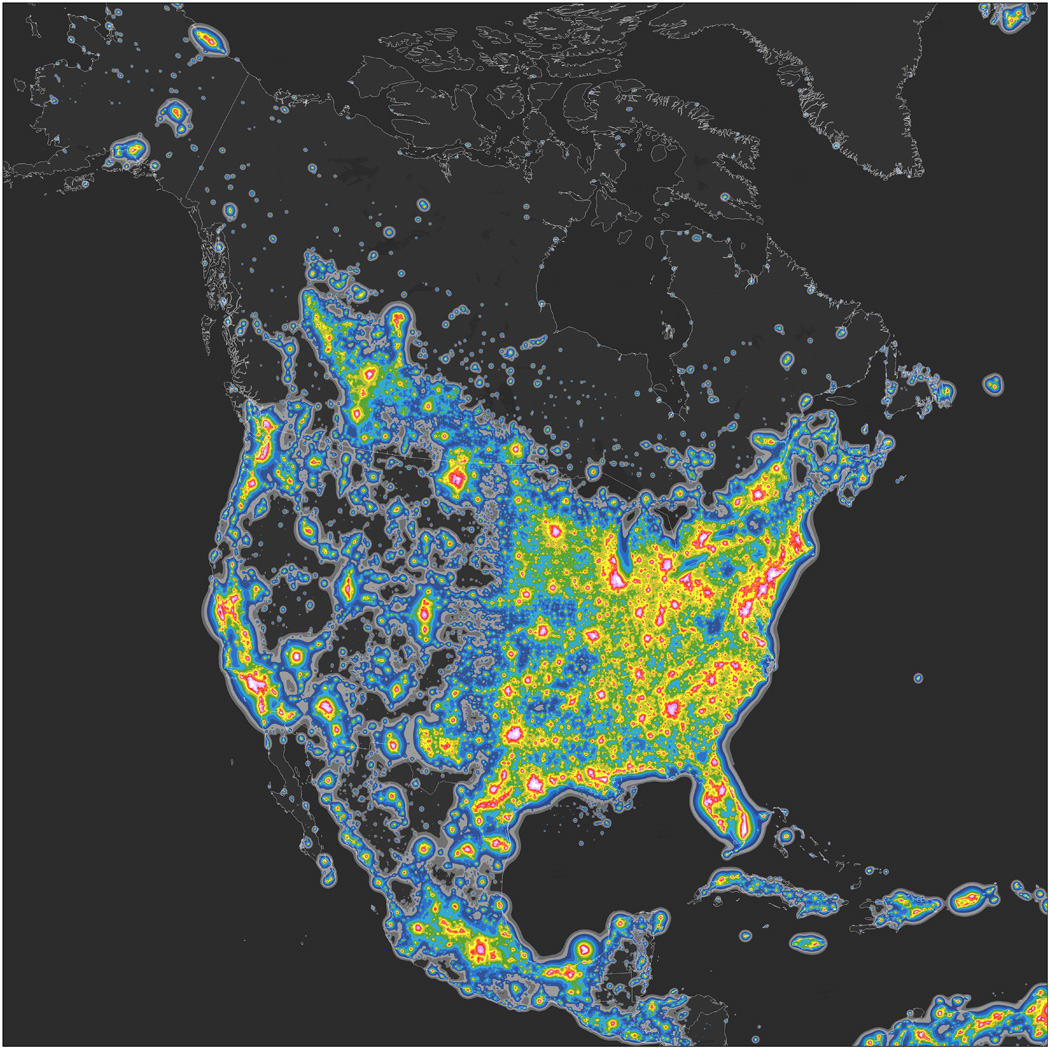
The New World Atlas of Artificial Night Sky Brightness
This resource presents a modern world atlas of global luminance. The content presented here can help you to better visualise and understand the extent to which light pollution is a global issue.
Light Pollution Map
This interactive light pollution map provides an array of overlay options that can help you to see the trends in light pollution over the past decade.